A Brief Detail On Cell Structure And Functions For NEET Biology
The cell is the smallest functional unit of the body. Cells are independent organic units that collectively build organisms. They are responsible for all the life processes like circulation, excretion, digestion, body growth, and movements.
Hence, they are the building blocks of life. They are microscopic in size and can be seen through microscopes. Robert Hooke discovered the cell, and its name was derived from the Latin word Cella meaning an enclosed chamber.
They have biological and structural importance that ensure the functioning of the body. The membrane-bound structures comprise cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell organelles. The chemical processing unit inside the cell is specialized to perform tasks.
A single cell can function by synthesizing, metabolizing, and replicating itself independently. The organisms may be unicellular or multicellular depending upon the number of cells. Cells are divided into two types, namely prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The structure of the organism becomes complex with increased cell structure. Test your knowledge by solving the Cell Structure and Organization NEET MCQ.
Some Facts About Cells
● The smallest cell is Mycoplasma.
● The ostrich egg is the largest cell.
● The smallest human cell is the RBC.
● The largest human cell is Ovum.
● Cells of the nervous system are the longest in the body.
Types Of Cells
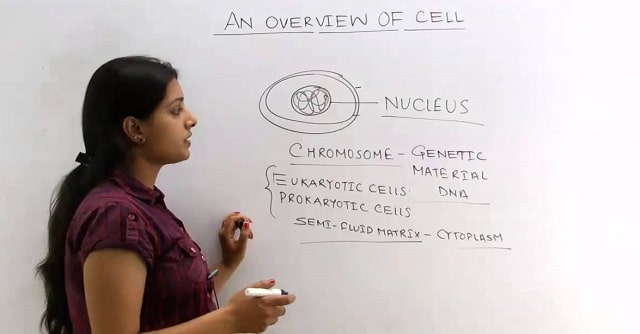
Cells can be classified based on their shape, size, and functions. The cells are divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes on the basis absence or presence of the nuclear membrane and the organelles.
Prokaryotes
• Membrane-bound nucleus
• Single chromosome
• Peptidoglycan cell wall
• Cell size: 0.5 µm to 100 µm
• Simple cell structure
• Bacteria, Mycoplasma, Blue- green algae
Eurkaryotes
• Membrane-bound nucleus present
• More than one chromosome
• Chitin made cell walls in fungi
• Cell size: 10 µm to 150 µm
• Complex cell structure
• Protista, plants, animals
Understanding The Cell Structure And Its Nature
All living organisms on earth are made up of cells. Cells are enclosed units having multiple organelles performing different functions. The cell structure includes cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles like the ribosome, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosome, and Golgi apparatus.
These organelles undergo multiple chemical reactions to contribute to the processes of the body. The cells communicate with the neighboring cells to build a cooperative network. The functions of different parts of a cell are given below.
● Cell Wall: It is the most important part of the plant cell. Cellulose, pectin, and hemicelluloses are responsible for making up the cell wall. It is also responsible for giving shape to the plant cell. It gives a structure to the cell and makes it strong.
● Cell Membrane: Cell membrane or plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane. It controls the intercellular movements of the materials. It is made up of proteins and lipids in which these proteins act as receptors to the incoming materials and act as carrier molecules. The transport across the membrane occurs using the fluid-mosaic model.
● Nucleus: Discovered by Robert Brown, Nucleus is a double membrane structure at the center of the cell. The space which is present between the two layers of the cell is the perinuclear space that has the endoplasmic reticulum on the outer sides. It controls the functioning of the cell. The ribosomes over the membrane are responsible for the movement of the RNA and protein molecules. The nucleus contains nucleolus, chromatin (deoxyribonucleic acid), and fluid nucleoplasm. The nucleus is responsible for reproduction and cell division. During cell division, chromatin is condensed to chromosomes for gene transfer.
● Cytoplasm: The cell fluid which is responsible for the chemical reactions in the cell is cytoplasm. The cell organelles reside in the cytoplasm. It allows the diffusion of the materials in the cell. Cell expansion, regeneration, and growth occur in the cytoplasm of the cell. The cytoplasm organelles are described below.
● Mitochondria: The powerhouse of the cell. It is a round or elongated structure that is responsible for energy production through cell respiration. It contains high proteins, fats, and enzymes.
● Golgi Apparatus: Discovered by Camillo Golgi, the Golgi apparatus is a site for glycoprotein and lipid synthesis. It acts as the messenger of the cell.
● Lysosomes: It is the covering of the Golgi apparatus responsible for the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It is the garbage collector that engulfs the cell wastes.
● Vacuoles: These are the sac-like structures holding the food, water, and cell wastes.
● Plastids: Members of the plant cells. Come up in three types: Chloroplasts,
● Leucoplasts And Chromoplast: A green pigment found in the plant leaves is Chloroplasts. It takes part in photosynthesis. The colors of the fruits and flowers are the responsibility of the chromoplast and leucoplasts stores starch, proteins, and fats.
● Endoplasmic Reticulum: A tubular network in the cytoplasm, which takes care of the movement of the proteins and molecules in the cell. It is present around the ribosomes. It allows the selective synthesis of molecules and processes them. These are of two types Rough Endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. These are responsible for lipid and protein production and cell detoxification.
Cell Functions
A cell is the smallest functional unit of the body. It performs various specialized functions in the body depending upon its structures. The crucial functions of the cell are mentioned below.
● It provides structure and support to the organisms.
● It facilitates growth by undergoing cell division by mitosis.
● It is responsible for maintaining the gene hierarchy of the organisms by regulating the DNA and protein synthesis.
● Energy production using photosynthesis is a crucial process to undergo chemical reactions.
● Enables transportation of the synthesized food, energy to and from the cell for regular functioning of the body. The processes of osmosis, diffusion, endocytosis, and exocytosis allow the movement of different materials in the cell. The wastes of the cell are discarded using the active and passive transport mechanisms.
Conclusion
Multiple-choice questions are the patterns of most competitive exams. This test element utilizes deep understanding, knowledge and develops problem-solving skills. Solving the MCQ after understanding the topic helps in the effective evaluation of the knowledge. Comprehensive knowledge of the topic is necessary to compete in NEET.
